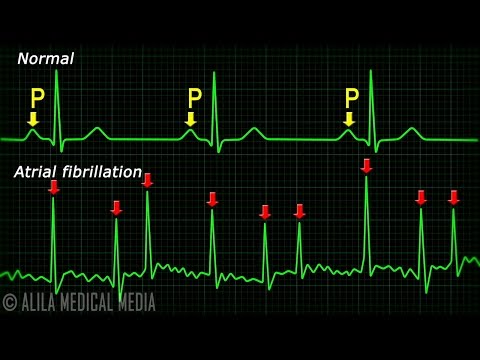
心房纖維性顫動大解密
alex 發佈於 2021 年 01 月 14 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字- v.t./i.棒;黏貼,張貼;堅持;伸出;忍受
- n. (c.)棍棒,棍枝,枝條
US /ɪk'strimlɪ/
・
UK /ɪkˈstri:mli/
- adv.極端地 ; 非常地;非常;從極端的角度來看
US /ˈmʌltəpəl/
・
UK /ˈmʌltɪpl/
- adj.多重的;多種的;多發性的;多重的
- n. (c.)多;多個的;乘數
- pron.多重的
US /ˈprɑːpərli/
・
UK /ˈprɔpəlɪ/