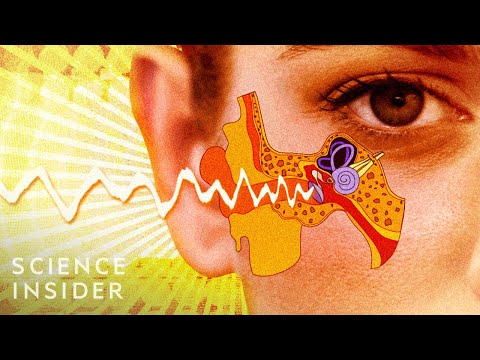
耳朵不只用作聽東西而已?竟然會影響我們的味覺和平衡感?(What's Inside A Human Ear?)
Fibby 發佈於 2020 年 02 月 22 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字- v.t./i.棒;黏貼,張貼;堅持;伸出;忍受
- n. (c.)棍棒,棍枝,枝條
US /ɪnˈkrɛdəblɪ/
・
UK /ɪnˈkredəbli/
- adv.令人難以置信的是;難以置信地;非常地;令人難以置信地
US /ˈprɑsˌɛs, ˈproˌsɛs/
・
UK /prə'ses/
- v.t.用電腦處理(資料);(依照規定程序)處理;處理;流程;加工;理解
- n. (c./u.)(規定的)程序;過程;進程;方法;法律程序;進程