字幕與單字
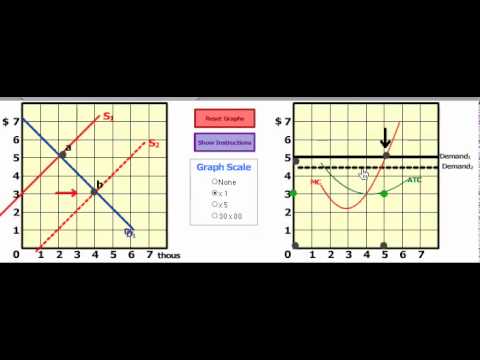
哈蒙教授用5分鐘解析完美競爭和長跑調整的方法。 (Professor Harmon Diagrams Perfect Competition and Long Run Adjustment in 5 mins)
00
Harrison Mia 發佈於 2021 年 01 月 14 日收藏
影片單字
average
US /ˈævərɪdʒ, ˈævrɪdʒ/
・
UK /'ævərɪdʒ/
- n. (c./u.)平均
- v.t.算出...的平均數
- adj.平均的;一般的,通常的;中等的
A2 初級多益中級英檢
更多 使用能量
解鎖所有單字
解鎖發音、解釋及篩選功能
