字幕與單字
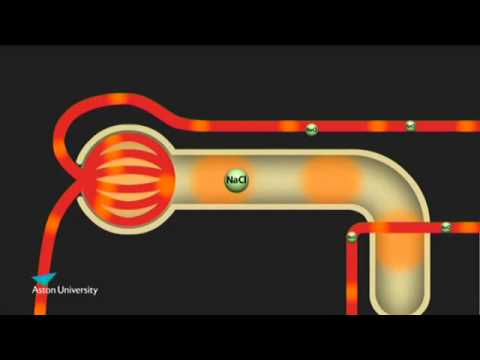
腎臟與逆流乘法。阿斯頓大學的藥理學教學 (The Kidney & the Counter Current Multiplier: Pharmacology teaching at Aston University)
00
柳夙芯 發佈於 2021 年 01 月 14 日收藏
影片單字
potential
US /pəˈtɛnʃəl/
・
UK /pəˈtenʃl/
- adj.可能的;潛在的;潛在的
- n. (u.)潛力,潛能
- n. (c./u.)潛力;潛能;潛在候選人;勢
A2 初級多益中級英檢
更多 使用能量
解鎖所有單字
解鎖發音、解釋及篩選功能
