字幕與單字
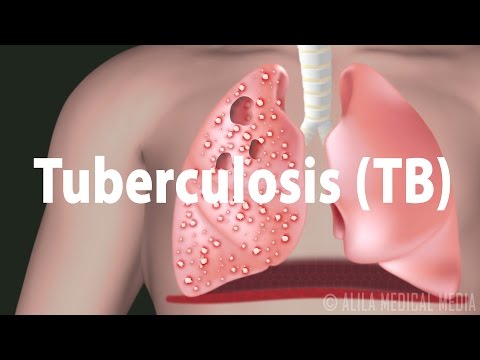
結核病。疾病的發展、潛伏和活動性感染; (Tuberculosis (TB): Progression of the Disease, Latent and Active Infections.)
00
Study English 發佈於 2021 年 01 月 14 日收藏
影片單字
process
US /ˈprɑsˌɛs, ˈproˌsɛs/
・
UK /prə'ses/
- v.t.用電腦處理(資料);(依照規定程序)處理;處理;流程;加工;理解
- n. (c./u.)(規定的)程序;過程;進程;方法;法律程序;進程
A2 初級多益中級英檢
更多 present
US /ˈprɛznt/
・
UK /'preznt/
- adj.出席;在場的;目前的
- n.正在進行的;現在時態;目前的;禮物
- v.t.介紹;主持;介紹;展現;贈送
- v.i.出現
A1 初級多益初級英檢
更多 progress
US /ˈprɑɡˌrɛs, -rəs, ˈproˌɡrɛs/
・
UK /'prəʊɡres/
- v.t./i.進展;進步;取得進展
- n. (u.)進展;發展;行進
- v.t.促進
A2 初級多益初級英檢
更多 使用能量
解鎖所有單字
解鎖發音、解釋及篩選功能
