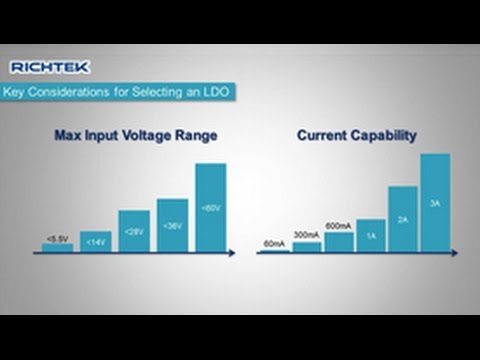
LDO功率耗散 (LDO Power Dissipation)
jmkuoa 發佈於 2021 年 01 月 14 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /məˈdʒɔrɪti, -ˈdʒɑr-/
・
UK /mə'dʒɒrətɪ/
- n. (c./u.)大多數 ; 過半數 ; 大半;成年;多數黨;多數票
US /ɪmˈpruv/
・
UK /ɪm'pru:v/
US /dɪˈtɚmɪn/
・
UK /dɪ'tɜ:mɪn/
US /ˈpræktɪkəl/
・
UK /ˈpræktɪkl/
- adj.實際的;實用的;實際的;務實的
- n.實作;注重實踐的人