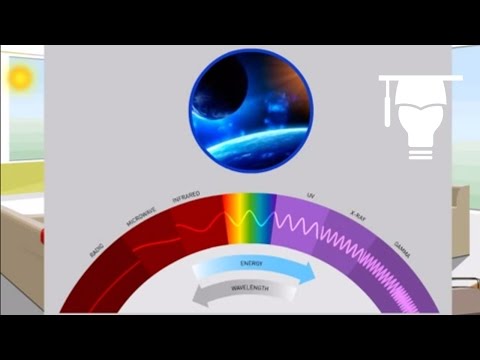
電磁頻譜 (The Electromagnetic Spectrum)
VoiceTube 發佈於 2021 年 01 月 14 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /ɪk'strimlɪ/
・
UK /ɪkˈstri:mli/
- adv.極端地 ; 非常地;非常;從極端的角度來看
US /rɪˈzʌlt/
・
UK /rɪ'zʌlt/
- n.(書的)篇;節;等分之一;(頭髮的)分線;角色;部分;角色
- v.t.將(頭髮)分線
- v.t./i.遠離;分離
- adj.部分的
US /ˈspɛktrəm/
・
UK /'spektrəm/
- n.光譜 ; 波譜;(看法、感覺等的)範圍,各層次