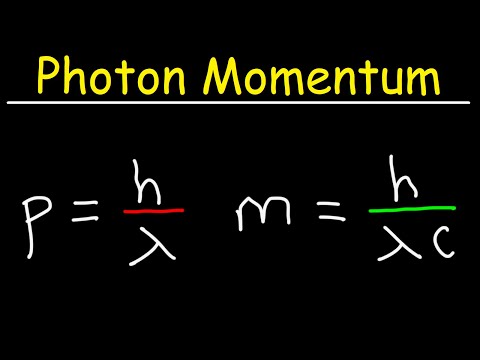
光子動量和有效品質 (Photon Momentum and Effective Mass)
kevin 發佈於 2024 年 10 月 02 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /ˈkɑnstənt/
・
UK /'kɒnstənt/
US /ˈnɛɡətɪv/
・
UK /'neɡətɪv/
- n.負電極的;否定詞;否定句;底片
- adj.消極的;負的;負面的;否定的;陰性的;負電的
US /ɪˈfɛktɪv/
・
UK /ɪˈfektɪv/
- v.t.宴請;款待;招待;治療;處理;對待;處理
- n. (c./u.)對待 ;;點心, 零嘴;特別的享受