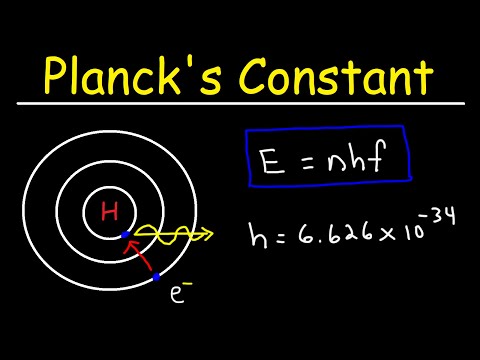
普朗克常數與黑體輻射 (Planck's Constant and BlackBody Radiation)
kevin 發佈於 2024 年 10 月 02 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /ɪˈvɛntʃuəli/
・
UK /ɪˈventʃuəli/
US /ˈmʌltəpəl/
・
UK /ˈmʌltɪpl/
- adj.多重的;多種的;多發性的;多重的
- n. (c.)多;多個的;乘數
- pron.多重的
US /ˈkɑnstənt/
・
UK /'kɒnstənt/
US /ˈnɛɡətɪv/
・
UK /'neɡətɪv/
- n.負電極的;否定詞;否定句;底片
- adj.消極的;負的;負面的;否定的;陰性的;負電的