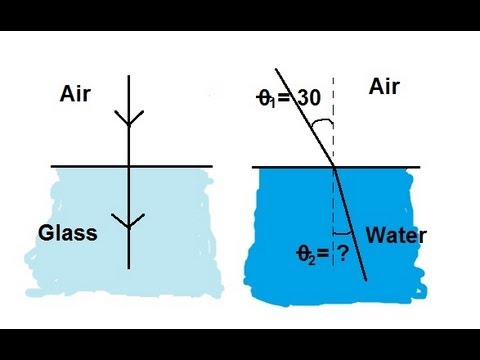
物理 52 折射與斯涅耳定律(共 11 頁,第 1 頁) 斯涅耳定律簡介 (Physics 52 Refraction and Snell's Law (1 of 11) Introduction to Snell's Law)
kevin 發佈於 2024 年 10 月 02 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /sɪɡˈnɪfɪkənt/
・
UK /sɪgˈnɪfɪkənt/
- v.i.是重要的
- n. (u.)物質
- n.件事情;問題;原因
- adj.異性戀者;異性戀的;率直的;立刻的;直的;整齊的
- adv.筆直地;立刻地;誠實地;直接地;立即
- n.異性戀者
- v.t./i.弄直
US /ˈkɑnˌsɛpt/
・
UK /'kɒnsept/