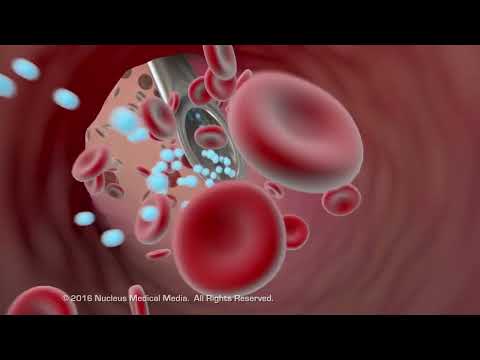
藥物如何被人體吸收 (How Medications Get Absorbed By Your Body)
2hs2q6gy8d 發佈於 2024 年 06 月 20 日  沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /ˈprɑsˌɛs, ˈproˌsɛs/
・
UK /prə'ses/
- v.t.用電腦處理(資料);(依照規定程序)處理;處理;流程;加工;理解
- n. (c./u.)(規定的)程序;過程;進程;方法;法律程序;進程
- n. (c./u.)公有地;公共用地;廣場
- adj.共用的;常見的;普通的;普遍的;粗俗的;普通名詞
US /ˈdʒɛnərəl/
・
UK /'dʒenrəl/
- adj.一種常見的做法,整體;籠統的;廣泛適用的;總指揮的
- n. (c.)將軍
- n. (c./u.)大眾;一般研究領域
US /əˈmaʊnt/
・
UK /ə'maʊnt/