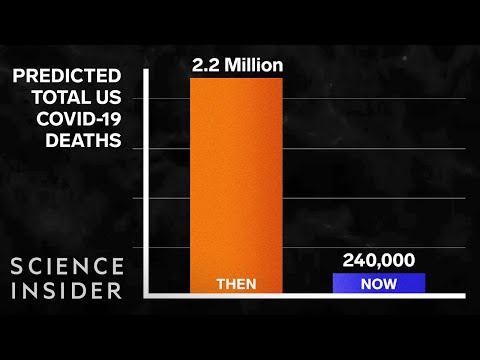
為什麼COVID-19的死亡預測永遠是錯誤的? (Why COVID-19 Death Predictions Will Always Be Wrong)
 沒有此條件下的單字
沒有此條件下的單字US /spɪˈsɪfɪk/
・
UK /spəˈsɪfɪk/
US /səˈsɛptəbəl/
・
UK /səˈseptəbl/
- adj.易感;易受影響的;易得病的;易受影響的;脆弱的
US /ˈkrɪtɪkəl/
・
UK /ˈkrɪtɪkl/
US /ˈæspɛkt/
・
UK /'æspekt/
- n. (c./u.)方面;觀點;(某物的)要素;特徵